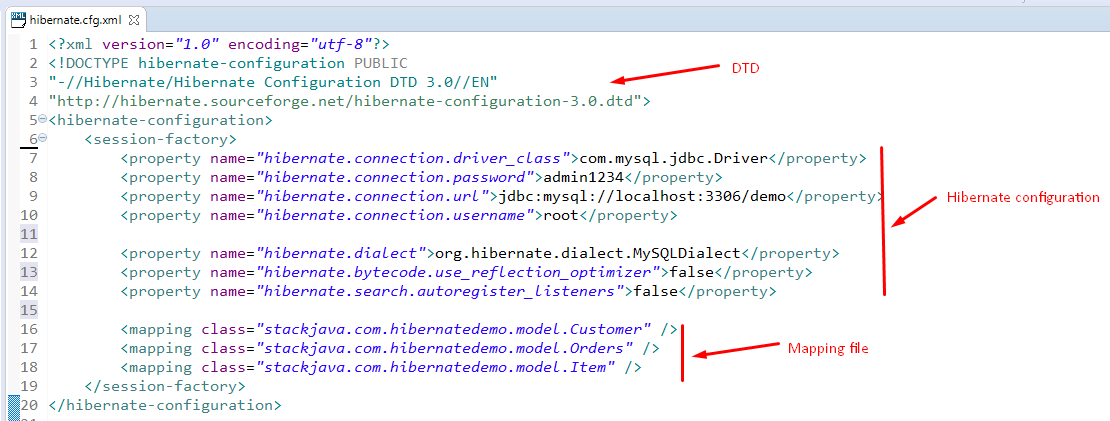
Hibernate configuration – Các thông tin cấu hình hibernate.
Ở các ví dụ trước chúng ta sử dụng thông tin kết nối tới database như database name, password… trong file hibernate.cfg.xml, đó là các thông tin cấu hình cho hibernate.
Các thông tin này thường đặt trong file hibernate.cfg.xml hoặc hoặc hibernate.properties, ở bài này chúng ta sẽ tìm hiểu một số các tham số khác dùng để cấu hình hibernate.
Hibernate configuration – Các thông tin cấu hình hibernate stackjava.com
Hibernate Properties
Các tham số cấu hình Hibernate JDBC Properties
| hibernate.connection.driver_class | The JDBC driver class |
| hibernate.connection.url | URL kết nối tới database. |
| hibernate.connection.username | Tên tài khoản dùng để kết nối tới database |
| hibernate.connection.password | Mật khẩu của tài khoản kết nối tới database |
| hibernate.connection.pool_size | Giới hạn số kết nối trong hibernate connection pool. |
Hibernate Datasource Properties
| hibernate.connection.datasource | datasource JNDI name |
| hibernate.jndi.url | URL của the JNDI provider |
| hibernate.jndi.class | Class của JNDI InitialContextFactory |
| hibernate.connection.username | database user |
| hibernate.connection.password | database user password |
Hibernate Configuration Properties
| hibernate.dialect | Dialect dùng để đánh dấu loại database sử dụng để hibernate tạo ra SQL cho phù hợp. (e.g. com.mysql.jdbc.Driver) |
| hibernate.show_sql | Ghi tất cả các câu truy vấn SQL ra console hoặc file log (e.g. true|false) |
| hibernate.format_sql | Định dạng câu SQL được ghi ra ở console/log (e.g. true|false) |
| hibernate.default_schema | Qualify unqualified table names with the given schema/tablespace in generated SQL. (e.g. SCHEMA_NAME) |
| hibernate.default_catalog | Qualifies unqualified table names with the given catalog in generated SQL. (e.g. CATALOG_NAME) |
| hibernate.session_factory_name | The org.hibernate.SessionFactory will be automatically bound to this name in JNDI after it has been created. (e.g. jndi/composite/name) |
| hibernate.max_fetch_depth | Sets a maximum “depth” for the outer join fetch tree for single-ended associations (one-to-one, many-to-one). A 0 disables default outer join fetching. (e.g. recommended values between 0 and 3) |
| hibernate.default_batch_fetch_size | Kích thước mặc định cho hibernate batch (e.g. khuyên dùng 4,8,16) |
| hibernate.default_entity_mode | Mode mặc định cho entity representation cho tất cả các session được mở từ sessionFactory, mặc định là pojo (e.g. dynamic-map| pojo) |
| hibernate.order_updates | Forces Hibernate to order SQL updates by the primary key value of the items being updated. This will result in fewer transaction deadlocks in highly concurrent systems. (e.g. true | false) |
| hibernate.generate_statistics | If enabled, Hibernate will collect statistics useful for performance tuning. (e.g. true | false) |
| hibernate.use_identifier_rollback | Nếu kích hoạt, giá trị id được tạo sẽ được reset về giá trị mặc định khi đối tượng bị xóa (e.g. true | false) |
| hibernate.use_sql_comments | Nếu kích hoạt, hibernate sẽ generate comment bên trong SQL để debug dễ hơn, mặc định là false (e.g. true | false) |
| hibernate.id.new_generator_mappings | Liên quan tới việc sử dụng @GeneratedValue, nó cho biết liệu việc cài đặt IdentifierGenerator có sử dụng cho javax.persistence.GenerationType.AUTO, javax.persistence.GenerationType.TABLE,
|
Hibernate JDBC and Connection Properties
| hibernate.jdbc.fetch_size | A non-zero value determines the JDBC fetch size (calls Statement.setFetchSize()). |
| hibernate.jdbc.batch_size | A non-zero value enables use of JDBC2 batch updates by Hibernate. e.g. recommended values between 5 and 30 |
| hibernate.jdbc.batch_versioned_data | Set this property to true if your JDBC driver returns correct row counts from executeBatch(). It is usually safe to turn this option on. Hibernate will then use batched DML for automatically versioned data. Defaults to false. (e.g. true | false) |
| hibernate.jdbc.factory_class | Select a custom org.hibernate.jdbc.Batcher. Most applications will not need this configuration property. (e.g. classname.of.BatcherFactory) |
| hibernate.jdbc.use_scrollable_resultset | Enables use of JDBC2 scrollable resultsets by Hibernate. This property is only necessary when using user-supplied JDBC connections. Hibernate uses connection metadata otherwise. (e.g. true | false) |
| hibernate.jdbc.use_streams_for_binary | Use streams when writing/reading binary or serializable types to/from JDBC. *system-level property* (e.g. true | false) |
| hibernate.jdbc.use_get_generated_keys | Enables use of JDBC3 PreparedStatement.getGeneratedKeys() to retrieve natively generated keys after insert. Requires JDBC3+ driver and JRE1.4+, set to false if your driver has problems with the Hibernate identifier generators. By default, it tries to determine the driver capabilities using connection metadata. (e.g. true|false) |
| hibernate.connection.provider_class | The classname of a custom org.hibernate.connection.ConnectionProvider which provides JDBC connections to Hibernate. (e.g. classname.of.ConnectionProvider) |
Hibernate configuration – Các thông tin cấu hình stackjava.com |
|
| hibernate.connection.isolation | Sets the JDBC transaction isolation level. Check java.sql.Connection for meaningful values, but note that most databases do not support all isolation levels and some define additional, non-standard isolations. (e.g. 1, 2, 4, 8) |
| hibernate.connection.autocommit | Enables autocommit for JDBC pooled connections (it is not recommended). (e.g. true | false) |
| hibernate.connection.release_mode | Specifies when Hibernate should release JDBC connections. By default, a JDBC connection is held until the session is explicitly closed or disconnected. For an application server JTA datasource, use after_statement to aggressively release connections after every JDBC call. For a non-JTA connection, it often makes sense to release the connection at the end of each transaction, by using after_transaction. auto will choose after_statement for the JTA and CMT transaction strategies and after_transaction for the JDBC transaction strategy. (e.g. auto (default) | on_close | after_transaction | after_statement) |
| hibernate.connection.<propertyName> | Pass the JDBC property <propertyName> to DriverManager.getConnection(). |
| hibernate.jndi.<propertyName> | Pass the property <propertyName> to the JNDI InitialContextFactory. |
Hibernate Cache Properties
| hibernate.cache.provider_class | The classname of a custom CacheProvider. (e.g. classname.of.CacheProvider) |
| hibernate.cache.use_minimal_puts | Optimizes second-level cache operation to minimize writes, at the cost of more frequent reads. This setting is most useful for clustered caches and, in Hibernate, is enabled by default for clustered cache implementations.(e.g. true|false) |
| hibernate.cache.use_query_cache | Enables the query cache. Individual queries still have to be set cachable. (e.g. true|false) |
| hibernate.cache.use_second_level_cache | Can be used to completely disable the second level cache, which is enabled by default for classes which specify a <cache> mapping. (e.g. true|false) |
| hibernate.cache.query_cache_factory | The classname of a custom QueryCache interface, defaults to the built-in StandardQueryCache. (e.g. classname.of.QueryCache) |
| hibernate.cache.region_prefix | A prefix to use for second-level cache region names. (e.g. prefix) |
| hibernate.cache.use_structured_entries | Forces Hibernate to store data in the second-level cache in a more human-friendly format. (e.g. true|false) |
| hibernate.cache.auto_evict_collection_cache | Enables the automatic eviction of a bi-directional association’s collection cache when an element in the ManyToOne collection is added/updated/removed without properly managing the change on the OneToMany side. e.g. true|false (default: false) |
| hibernate.cache.default_cache_concurrency_strategy | Setting used to give the name of the default org.hibernate.annotations.CacheConcurrencyStrategy to use when either @Cacheable or @Cache is used. @Cache(strategy=”..”) is used to override this default. |
Hibernate Transaction Properties
| hibernate.transaction.factory_class | The classname of a TransactionFactory to use with Hibernate Transaction API (defaults to JDBCTransactionFactory).e.g. classname.of.TransactionFactory |
| jta.UserTransaction | A JNDI name used by JTATransactionFactory to obtain the JTA UserTransaction from the application server. (e.g. jndi/composite/name) |
| hibernate.transaction.manager_lookup_class | The classname of a TransactionManagerLookup. It is required when JVM-level caching is enabled or when using hilo generator in a JTA environment. (e.g. classname.of.TransactionManagerLookup) |
| hibernate.transaction.flush_before_completion | If enabled, the session will be automatically flushed during the before completion phase of the transaction. Built-in and automatic session context management is preferred (e.g. true | false) |
| hibernate.transaction.auto_close_session | If enabled, the session will be automatically closed during the after completion phase of the transaction. Built-in and automatic session context management is preferred (e.g. true | false) |
Các thuộc tính khác
| hibernate.current_session_context_class | Tùy chỉnh phạm vi cho session hiện tại (e.g. jta | thread | managed | custom.Class) |
| hibernate.query.factory_class | Chọn cài đặt cho HQL parser (e.g. org.hibernate.hql.internal.ast.ASTQueryTranslatorFactory or org.hibernate.hql.internal.classic.ClassicQueryTranslatorFactory) |
| hibernate.query.substitutions | (e.g. hqlLiteral=SQL_LITERAL, hqlFunction=SQLFUNC) |
| hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto | Tự động validate hoặc export schema DDL khi SessionFactory được tạo. Với create-drop thì database schedule sẽ bị xóa khi SessionFactory bị đóng. (e.g. validate | update | create | create-drop) |
| hibernate.hbm2ddl.import_files | Chứa các file sql (phân cách bởi dấu phẩy) được thực thi khi SessionFactory được tạo. (e.g. abc.sql, import.sql) |
| hibernate.hbm2ddl.import_files_sql_extractor | The classname of a custom ImportSqlCommandExtractor (defaults to the built-in SingleLineSqlCommandExtractor). This is useful for implementing dedicated parser that extracts single SQL statements from each import file. Hibernate provides also MultipleLinesSqlCommandExtractor which supports instructions/comments and quoted strings spread over multiple lines (mandatory semicolon at the end of each statement). (e.g. classname.of.ImportSqlCommandExtractor) |
| hibernate.bytecode.use_reflection_optimizer | Enables the use of bytecode manipulation instead of runtime reflection. This is a System-level property and cannot be set in hibernate.cfg.xml. Reflection can sometimes be useful when troubleshooting. Hibernate always requires javassist even if you turn off the optimizer. (e.g. true | false) |
| hibernate.bytecode.provider | Hiện tại, javassist chỉ hỗ trợ bytecote. (e.g. javassist) |
Hibernate configuration – Các thông tin cấu hình hibernate stackjava.com
References:
https://docs.jboss.org/hibernate/orm/3.3/reference/en/html/index.html
https://docs.jboss.org/hibernate/orm/5.0/manual/en-US/html/ch03.html